When embarking on the journey to become a lawyer, one of the first questions that may arise is: What’s the difference between law school and law college? While these terms are often used interchangeably, they refer to different aspects of legal education. Understanding the distinction can help you make an informed decision about where to pursue your legal education, and ultimately, which path aligns best with your career goals.
Let’s break down the differences between law schools and law colleges, and help you decide which one is right for you.
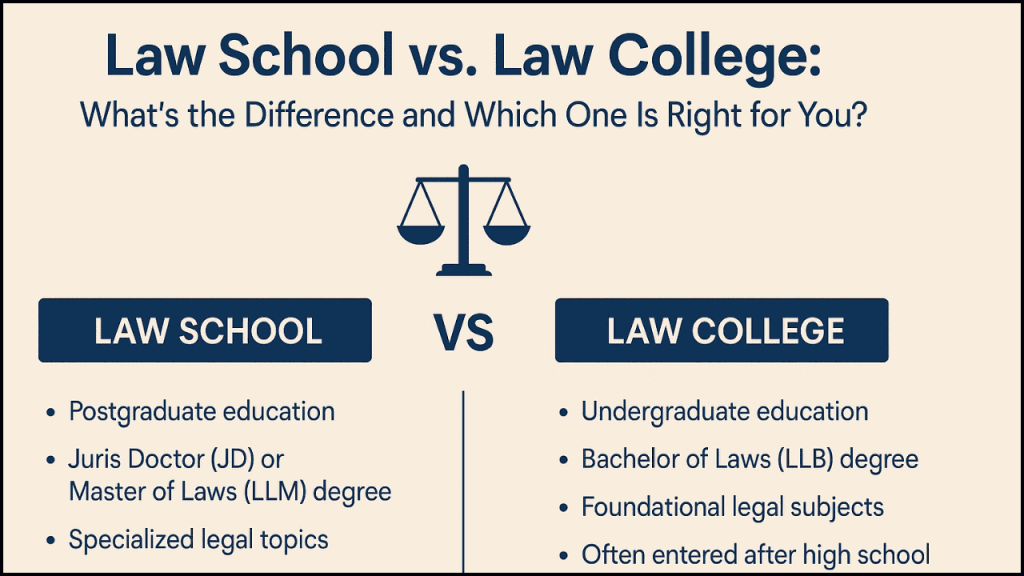
What is a Law School?
A law school is a professional institution that provides legal education after completing an undergraduate degree. In many countries, law schools are specifically designed to offer specialized training that prepares students for legal practice and licensure. Law schools focus on advanced legal topics and are typically part of universities or institutions offering postgraduate degrees.
Key Features of Law Schools:
- Postgraduate Education: Most law schools admit students who have already completed an undergraduate degree in any discipline (arts, science, or business).
- Advanced Curriculum: Law schools focus on specialized courses like constitutional law, corporate law, international law, intellectual property, and more.
- Legal Training: Law schools provide the knowledge and skills required for bar exams and legal practice, such as legal research, writing, and oral advocacy.
- Professional Environment: Law schools tend to have closer links to the legal profession, offering opportunities for internships, externships, and networking within the legal field.
Notable Law Schools Around the World:
- Harvard Law School (USA)
- Oxford University Faculty of Law (UK)
- Yale Law School (USA)
- University of Sydney Law School (Australia)
Law schools primarily offer graduate-level programs like the Juris Doctor (JD) or Master of Laws (LLM). They also provide opportunities to study for specific legal certifications or credentials.
What is a Law College?
A law college refers to an institution that offers legal education primarily at the undergraduate level. In some countries, law colleges serve as standalone institutions, while in others, they may be part of a larger university or college. Law colleges are the stepping stones to becoming a lawyer, as they offer the initial education required to enter the legal profession.
Key Features of Law Colleges:
- Undergraduate Education: Law colleges usually offer Bachelor of Laws (LLB) programs. Students entering law colleges typically do not need prior legal training and pursue their law degree immediately after completing high school or an undergraduate degree.
- Foundation Legal Curriculum: The curriculum at law colleges focuses on foundational legal subjects such as criminal law, contract law, property law, and family law.
- Pre-Professional Education: Law colleges provide the academic foundation needed for students to pursue advanced legal studies, whether it be a law school (for professional law degrees) or a bar exam for licensure.
- Licensure Readiness: Graduates of law colleges can directly prepare for legal practice by applying for bar exams or entering into internships or clerkships with law firms.
Notable Law Colleges Around the World:
- National Law School of India University (NLSIU), Bangalore (India)
- University of Delhi Faculty of Law (India)
- Faculty of Law, University of Cambridge (UK)
- University of Mumbai Department of Law (India)
Law colleges are ideal for individuals who wish to pursue a professional law career directly without first having to obtain a general degree in another field.
Key Differences Between Law School and Law College
- Level of Education:
- Law School: Postgraduate level education after completing a bachelor’s degree.
- Law College: Undergraduate level education, typically for those entering legal studies right after high school or after completing a non-legal undergraduate degree.
- Degree Offered:
- Law School: Offers advanced degrees like Juris Doctor (JD) or Master of Laws (LLM).
- Law College: Offers undergraduate degrees like Bachelor of Laws (LLB).
- Curriculum Focus:
- Law School: Specializes in advanced legal topics and provides deeper professional training for future lawyers.
- Law College: Focuses on building a foundational understanding of law, covering a range of core legal subjects.
- Admission Requirements:
- Law School: Requires a previous undergraduate degree. Students may need to take an entrance exam like the LSAT (in the USA) or the LNAT (in the UK).
- Law College: Usually admits students after completing high school, sometimes after passing a national or state-level law entrance exam.
- Professional Orientation:
- Law School: More geared towards producing practicing lawyers, with a focus on preparing students for the bar exam and legal careers.
- Law College: Prepares students for basic legal practice or to continue their legal education at the postgraduate level.
Which One Is Right for You?
The decision between attending a law school or a law college depends largely on your academic background and career goals.
When to Choose Law College:
- If you are interested in starting your legal education immediately after high school or an undergraduate degree in a non-legal field.
- If you are aiming to become a lawyer and are looking for an institution that offers a foundational legal education with the opportunity to take the bar exam.
- If you are planning to specialize in one area of law or gain practical experience through internships early in your career.
When to Choose Law School:
- If you already hold an undergraduate degree and are interested in pursuing a more specialized legal education at a postgraduate level.
- If you want to attend a prestigious institution and gain deep knowledge in specific legal fields.
- If you are focused on preparing for high-level roles within the legal profession, such as becoming a corporate lawyer, judge, or legal consultant.
Final Thoughts
While law schools and law colleges both provide essential legal education, they cater to different stages of your legal career. Law colleges offer a foundational education, while law schools provide advanced, professional training. The right choice for you depends on your educational background, career aspirations, and the type of legal career you want to pursue. Whether you’re entering the profession right after high school or looking to specialize after obtaining a degree, both options offer valuable pathways to becoming a lawyer.